The MOPAN Approach
MOPAN tells the story of an organisation’s current performance based on a methodological framework underpinned by the MOPAN Hypothesis. MOPAN’s methodology has evolved over time to remain relevant, timely and useful for the multilateral system.
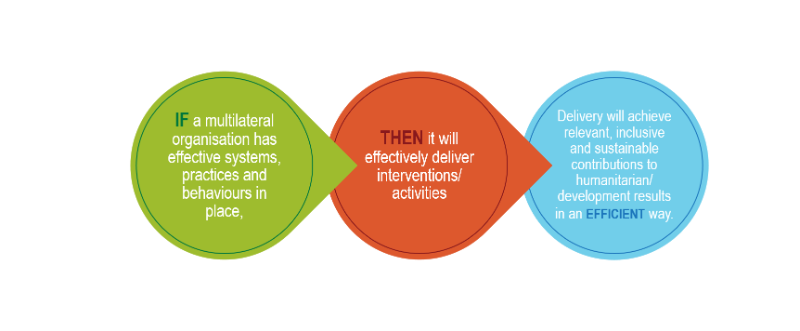
The MOPAN Hypothesis
MOPAN 3.1
The latest version of MOPAN's methodology, MOPAN 3.1, is used for organisational assessments beginning in 2020. It introduces integrated measures reflecting important mulitlateral agendas such as The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, preventing and responding to sexual exploitation, abuse, and harassment, and the United Nations Development System Reform.
Evolution of The MOPAN Approach
Since 2003, MOPAN has assessed organisations using five different approaches to conduct assessments.
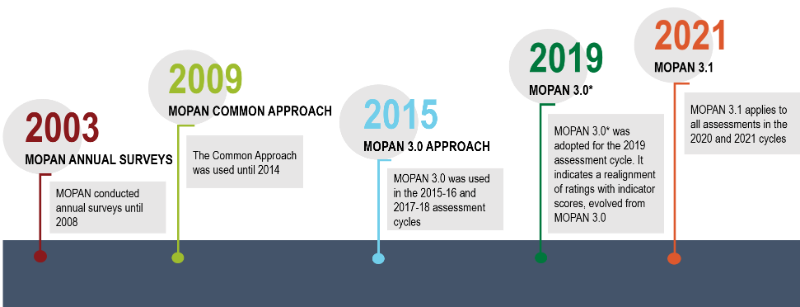
The progression to MOPAN 3.0*, as well as application of MOPAN 3.1, reflect the growing demand for organisational performance in the multilateral system. Underlying scores and approach to scoring have however, remained unchanged.
Anatomy of a MOPAN Assessment
Contextual analysis
A MOPAN assessment provides a holistic diagnostic of an organisation’s performance taking into account the history, mission, context, trajectory and journey of the organisation. It presents analytical justifications for ratings and provides multidimensional insights on organisations based on the MOPAN indicator framework.
MOPAN assessments are conducted through an independent, rigorous process and take a collaborative approach to ensure that the findings resonate with an organisation and its stakeholders. MOPAN assessments aim to build organisational learning in an iterative process that makes reporting accessible, and leaves an 'audit trail' of findings.
Sources
MOPAN assessments draw on multiple lines of evidence (documentary, survey, and interviews) from sources within and outside an organisation to validate and triangulate findings against the MOPAN indicator framework. The assessment process efficiently builds layers of data by using different streams, which reduces the burden on the organisation being assessed.
MOPAN Performance Areas
MOPAN 3.1 assesses multilateral organisation performance across five performance areas. Four areas - Strategic, Operational, Relationship and Performance Management - relate to organisational effectiveness, while the fifth reports on achievement of Results, in relation to the mandate of the organisation.

Co-ordination
The MOPAN Secretariat, the key interface for all parties involved in the assessment process, is responsible for overseeing and coordinating assessments of multilateral organisations. The Secretariat ensures that assessments are objective and impartial; and is responsible for their quality, including their analytical rigour and the diligence of the process.
Institutional Leads (ILs) are designated MOPAN members that facilitate the assessments of multilateral organisations alongside the Secretariat. ILs lead the assessment, championing and supporting the assessment process from inception to completion.
MOPAN works with a selected group of external service providers to carry out assessments. Service providers gather information at an organisations’ headquarters and in countries where they operate, conducting the analysis that leads to the to drafting of the assessment report.
Delimitations
A MOPAN assessment is neither an external institutional audit nor an evaluation; it cannot comprehensively examine all organisational operations or processes, provide a definitive picture of achievements and performance, or comprehensively document or analyse on-going organisational reform processes.
MOPAN assessments are stand-alone products that do not compare organisations nor are they meant to be used for this purpose.

